The foods we choose have a surprisingly direct impact on the health of the nervous system. Choose these anti-inflammatory foods when working to reverse nerve damage.
Your body is built with the ability to heal itself. Under normal circumstances (and, admittedly, to a relatively limited degree), your body self-repairs when it becomes damaged. This doesn’t mean you can re-grow a lost limb, like Wolverine from the X-Men comics.
What it does mean is that while your body can repair tissues like skin, bones, muscles, and nerves, it must have the right materials to do so. Say you wanted to repair a wall. You’d need the right materials and the right knowledge. Same with the repair of nerves.
So what are these materials needed to repair nerves, you are probably asking.
Nerves are very delicate parts of our body and therefore rather easily damaged. Whether they are damaged from chemicals, like medications or chemotherapy, or toxins, like alcohol and smoking or household toxicity, or any of the over 100 identified causes of nerve damage.
Chronic inflammation is what has been more recently identified as the common factor in nearly all of our modern diseases.
When the body becomes chronically inflamed by the very same factors that cause nerve damage, it is the chronic inflammation that hinders the body from healing itself. And it also is the chronic inflammation that alters the immune system in a way that continues to damage the nerves further.
Here is the good news. We have also discovered that chronic inflammation very much can be reversed. And when we reverse chronic inflammation, we reverse its effects.
Adopting anti-inflammatory foods for nerve health is the first place to start relieving the immune system of an inflammatory response and allowing it to shift towards healing.
Add these anti-inflammatory foods to your diet to replace inflammatory foods.
Dark Leafy Greens (Folate)
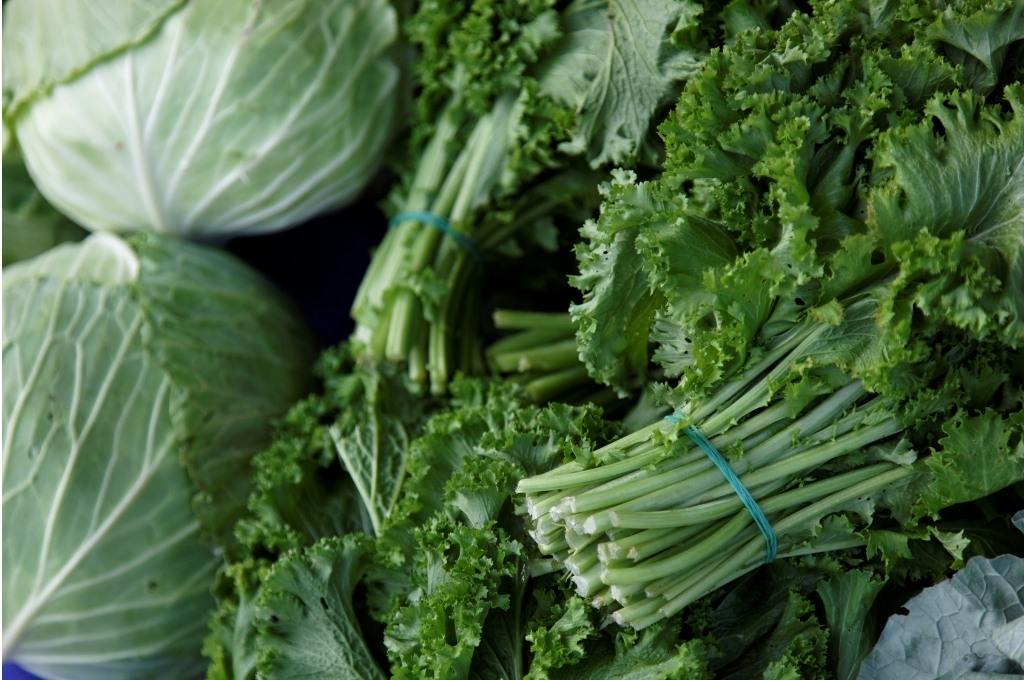

Darker leafy greens are packed with folate, also known as vitamin B9. Folate plays a leading role in the state of your nervous system, as it helps to promote nerve health in very direct ways.
Oxidative stress is a major precursor to inflammation, which leads to issues like nerve damage. Antioxidants, therefore, are helpful in the fight against nerve damage by helping to neutralize the damaging inflammation.
Dark leafy greens are packed with the type of antioxidants that neutralize compounds known as “free radicals” in the bloodstream, which cause oxidative stress that often leads to an inflammatory response.
A folate deficiency has been shown to lead to peripheral neuropathy, which makes this nutrient important to watch to avoid peripheral neuropathy or its progression.
These foods are also rich in magnesium, which is another helpful nutrient, as it helps your body send oxygen-rich blood to your muscles and nerve endings.
Try adding these anti-inflammatory dark leafy greens into your diet daily.
- Kale
- Spinach
- Collard greens
- Arugula
- Mustard greens
- Swiss chard
It’s always best to get nutrients from the natural whole form in foods. But if you’re not a veggie person, try supplementing with a high-quality folate (in the form of methyltetrahydrofolate) approximately 1,000 mg per day.
Seeds and Nuts (Omega-3)
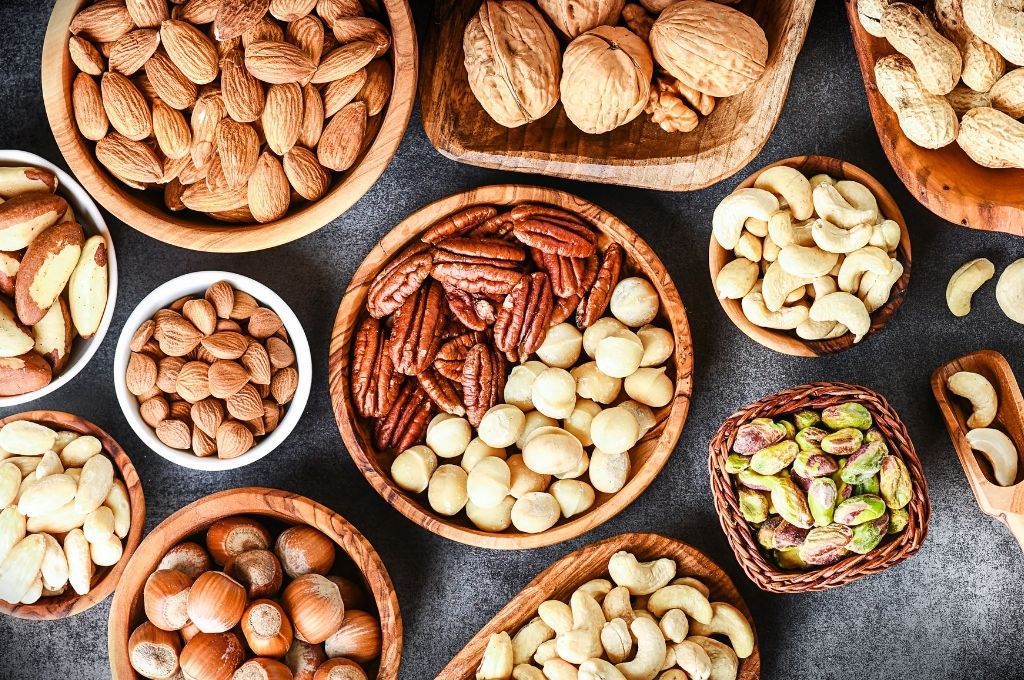

Omega-3 fatty acids are also known as polyunsaturated fatty acids, and it’s one of the kinds of fats that are quite healthy — especially where your nerve endings are concerned.
Many of your nerves are covered by a layer known as the myelin sheath. Not only does this part of your nerves offer up some valuable protective covering, but it also helps to encourage connectivity. This means it helps your nerves send their messages throughout your body quickly and accurately.
Some forms of neuropathy actually set their sights on the myelin sheath specifically, such as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Meaning, the immune system explicitly targets this protective covering, which is made up of fats and proteins.
This means that by introducing more of the right kinds of fats and proteins into your diet — like omega-3 fatty acids — the more your body has what it needs to produce more of the protective myelin sheath.
Try adding seeds and nuts like these into your diet for the health of your myelin sheath.
- Almonds Shop Almonds
- Walnuts Shop Walnuts
- Pumpkins seeds Shop Pumpkin Seeds
- Brazil nuts Shop Brazil Nuts
- Flax seeds Shop Flax Seeds
- Chia seeds Shop Chia Seeds
Seafood (Omega-3)
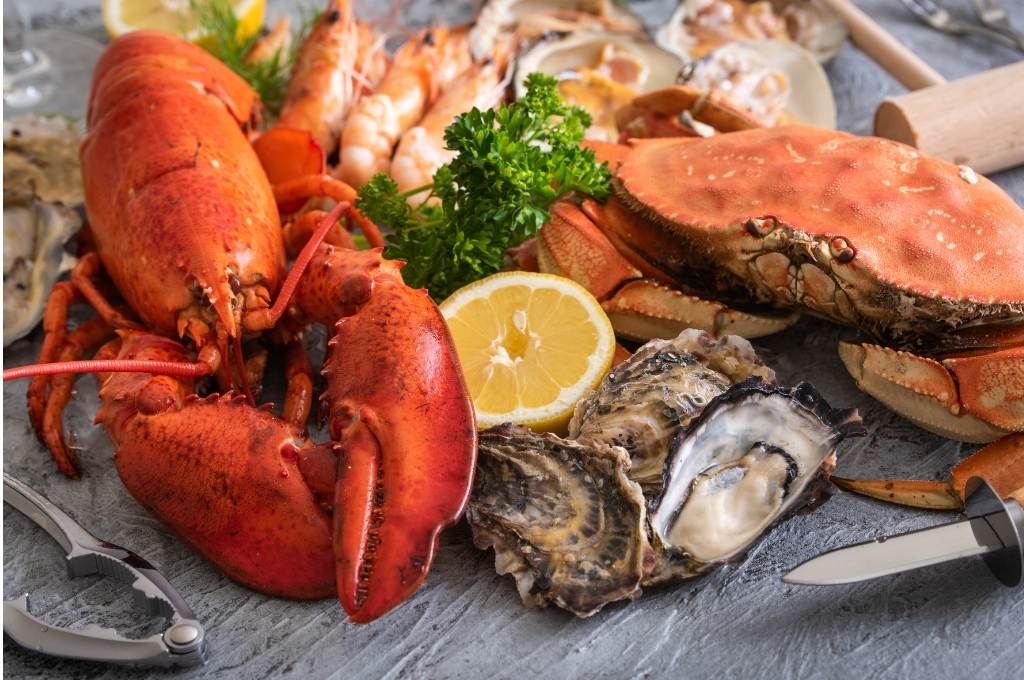

Another reliable source for healthy polyunsaturated fats can be the right types of seafood — specifically, fish that are rich in fatty omega-3 fish oils. Fish that are high in fatty oils like tuna, trout, and salmon are a great way to give your body a boost in maintaining the protective myelin sheath.
Additionally, fish oils have been shown to act as a powerful anti-inflammatory agent, meaning the right seafood dishes can go a long way towards helping fight back against chronic systemic inflammation.
Fish oils are also good at encouraging liver function, which helps the body rid itself of toxins that can build up over time. Ironically enough, you also need to watch out for toxins when you’re picking out your next fish dinner.
Certain types of fish — mostly tuna, swordfish, mackerel, and marlin — can contain high levels of mercury, absorbed into their bodies and accumulated over time, via their oceanic environment. A good rule of thumb is that older and larger fish tend to be more risky when it comes to mercury exposure, simply because these animals have had more time to absorb and accumulate the dangerous and toxic heavy metal.
“You should eat at least two servings a week of fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, or herring. Aim for fish that are high in two different omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), each of which provides unique health benefits,” says Dr. JoAnn Manson, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Don’t like fish? High-quality professional-grade omega-3 supplements with DHA and EPA are the next best thing. But not just any cheap fish oil off the shelf, of which many brands are known to contain heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyl. And while the exposure is minimal, with long-term use contaminants may result in long-term health complications.
Grass-Fed Beef (Alpha-Lipoic Acid)
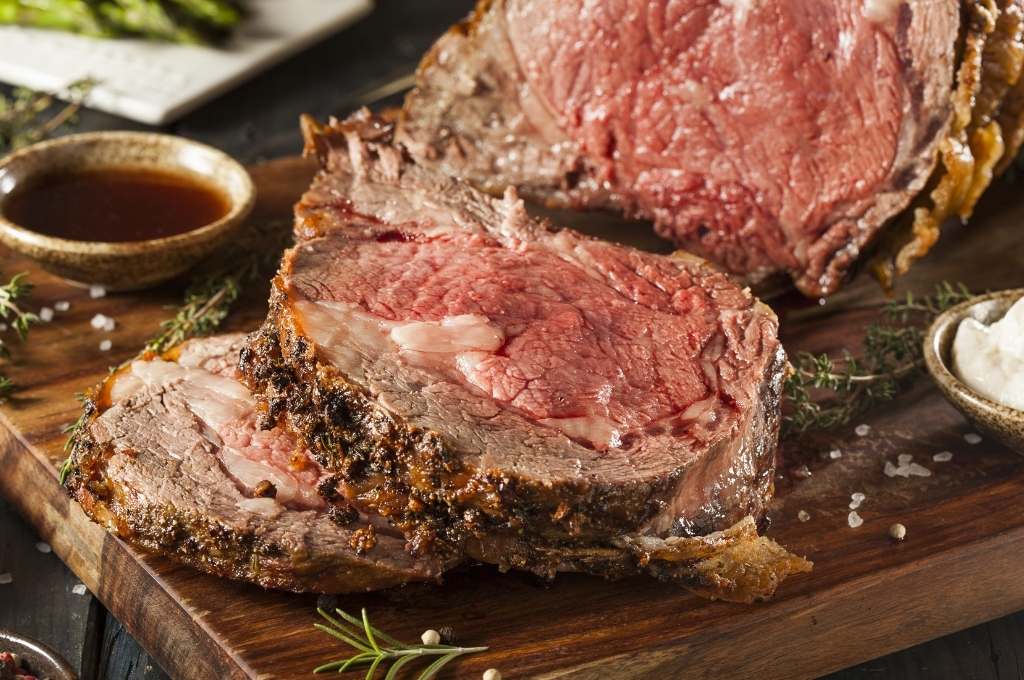

One of the most common contributors to peripheral neuropathy is insulin resistance.
Elevated blood sugar changes the chemical composition of your blood in a way that is damaging to nerve endings. With the high incidence of insulin resistance, it is no surprise that diabetic neuropathy is among the most commonly seen types.
Alpha-lipoic acid, then, is helpful in the fight against peripheral nerve damage because it’s something of a two-for-one. Not only does alpha-lipoic acid help maintain blood sugar levels, but it has been shown to lower inflammation, too.
Because it acts like an antidote to oxidative stress and inflammation, alpha lipoic acid fights damage done to the blood vessels, brain, neurons, and organs like the heart or liver.
This means it offers numerous benefits throughout the whole body, from naturally treating Alzheimer’s disease to controlling liver disease and nerve disease.
Animal products like grass-fed red meat and organ meats are great sources of alpha-lipoic acid, but some plant foods also contain it.
Therefore, increasing your levels of alpha-lipoic acid isn’t that hard by simply adding these varieties of foods into your diet daily.
- Grass-fed beef
- Organ meats (such as liver, hearts, and kidneys from chicken and beef)
- Yams
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Green peas
However, once nerve damage has started setting in, higher therapeutic doses may be necessary to improve blood sugar, reduce inflammation, and improve nerve function.
That said, supplements can pack up to 1,000 times more alpha-lipoic acid than food sources.
Studies have discovered that supplementing with alpha-lipoic acid may reduce symptoms of neuropathy after three weeks of alpha-lipoic acid at 600mg per day, and may promote nerve growth after six weeks of use.
R-lipoic acid is the natural form of alpha-lipoic acid and is thought to be more effective than the synthetic form, S-lipoic acid.
Legumes (Magnesium)
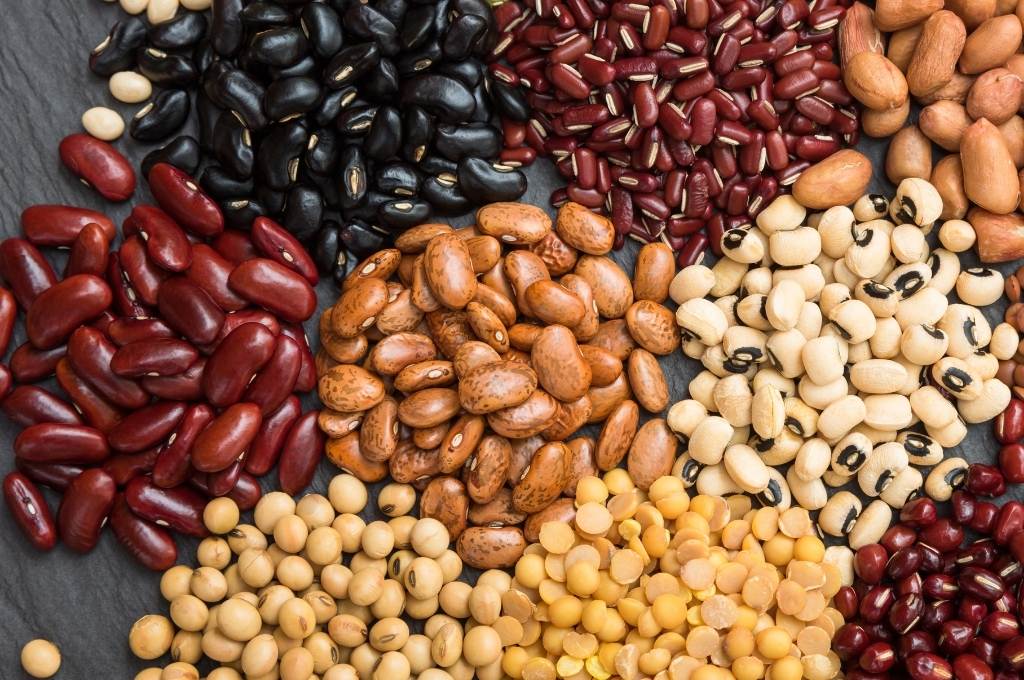

Magnesium is another one of those essential nutrients when it comes to neuropathy because it is necessary for many nerve-related functions.
A study published in 2016 reported that magnesium is significantly beneficial when it comes to restoring nerve function, especially when it comes to patients suffering from peripheral nerve damage. Magnesium was found to aid in the process of something known as axonal regeneration — or the regrowing of your nerve endings, in other words.
Patients with nerve damage were shown to experience increased axonal functioning when they took magnesium, showing that it plays a key role when it comes to nerve health.
Yet another study showed that magnesium offers up a handful of diabetes-specific benefits as well, like helping to metabolize glucose, and thereby maintaining proper blood sugar levels.
Magnesium can be found naturally in legumes.
Legumes are a family of nutrient-dense plants that include lentils, beans, chickpeas, peas and soybeans.
Just a 1-cup serving of cooked black beans contains an impressive 120 mg of magnesium, which is 30% of the recommended daily intake.
Because legumes are rich in fiber and have a low glycemic index (GI), they may lower cholesterol, improve blood sugar control, and decrease heart disease risk.
- Lentils Shop lentils
- Chickpeas Shop chickpeas
- Black-eyed peas Shop black-eyed peas
- Pinto bean Shop pinto beans
- Lima beans Shop lima beans
- Navy beans Shop navy beans
- Black beans Shop black beans
Magnesium is so vital for the movement of electrical impulses in the nervous system, a deficiency can be noticed with symptoms such as:
- Tingling
- Cramping
- Numbness
- Twitching
Magnesium is also helpful in alleviating pain associated with muscles and nerves. A key way pain is felt is through the excessive stimulation of a brain chemical (called NMDA). The few medications that decrease this pain-transmitting chemical cause significant side effects. Magnesium calms pain without the toxicity of these medications.(1)
If experiencing these symptoms, it may be worth testing magnesium supplementation for about three months, alongside healthy lifestyle choices, and taking note of any improvements.
The average recommended daily amount of magnesium is 320 mg for women and 420 mg for men (2).
However, a therapeutic dose when used in the case of magnesium deficiency is 400-800 mg per day.
Choosing a type of magnesium can be daunting, given that there are at least 11 supplement varieties on the shelves.
Here are the top varieties of magnesium used by people with neurological symptoms.
- Magnesium oxide is mostly used for temporary relief of constipation.
- Magnesium citrate may boost mood (3), improve blood sugar (4), and decrease chronic pain (5)
- Magnesium glycinate has a calming effect, good for reducing chronic pain, and improving sleep, relaxation, and mental calm (6).
- Magnesium malate is best used for generalized pain (7), muscle function (8), and bowel regularity.
Broccoli (Chromium)

Chromium makes insulin function more efficiently and has been found to be helpful for people with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance (prediabetes). There is good evidence showing that chromium can lower glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity, as well as aid in weight loss.
As a result, chromium can help you maintain safe blood sugar levels that encourage healthy peripheral nerve endings.
It also helps your body with the metabolization of fats and proteins — these are essential components of the myelin sheath, meaning chromium not only helps to encourage healthy nerves, but it boosts your body’s ability to protect them, as well.
Broccoli is a great source of chromium, readily available and easy to prepare, making it a perfect food to keep on hand when trying to adjust your diet to be more neuropathy-friendly.
Chromium supplements are one of the first choices among many healthcare providers for people with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes to lower glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
The doses used in clinical studies vary, but approximately 400 to 1,000 micrograms daily, split among three times a day is generally recommended by health practitioners.
Ginger (Antioxidant)

Ginger acts as a powerful antioxidant, relieving chronic inflammation in the body, which can provide relief from the types of pain that can come along with peripheral nerve damage.
Ginger oil contains a compound called zingiber, which possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties. Zingiber, therefore, may help reduce neuropathic pain that results from inflammatory conditions.
Ginger is among some of the herbs that the medical community has been investigating for their beneficial properties for nerve health.
To routinely incorporate ginger into your diet:
- Add peeled, fresh ginger to vegetables (like broccoli) and stir-fries Shop fresh ginger
- Drink ginger root herbal tea Shop ginger root tea
- Add peeled, fresh ginger to fruit or vegetable smoothies
Diet Choices Go a Long Way Towards Healthy Nerves
There’s no two ways around it — the foods we eat have a dramatic impact on the status of our nervous system, be it healthy or otherwise.
Learning which foods can tame chronic inflammation and provide nerves with essential nutrients goes a long way toward nerve health.
Top Red Light Therapy Devices for At-Home Neuropathy Treatment

Encouraging nerve regeneration is key to recovering from neuropathy. There are many ways for helping…
Neurochondria by Thorne: A Supplement for Nerve Pain Review

It’s pretty safe to say that the symptoms of neuropathy and nerve pain may very…
Complete Guide to CBD for Neuropathy

CBD seems to be in everything these days — oils, lotions, drinks, gummies, sprays, supplements,…
4 Clean CBD Brands You Can Trust

CBD has grown in popularity over recent years, especially for anxiety, pain, and sleep disorders.…
8 Best Supplements for Neuropathy
We know that nutritional supplements -- in addition to a healthy diet -- can help…
What Does My Peripheral Neuropathy Diagnosis Mean?

It’s a mouthful. Confused by what it even means? If you have a peripheral neuropathy…
Confused By Your Symptoms? Here’s What They Mean.

Peripheral neuropathy was long known to be a nerve disease that causes symptoms like tingling,…
What Causes Neuropathy?

Neuropathy is very common. It is estimated that about 25% of Americans will be affected.…